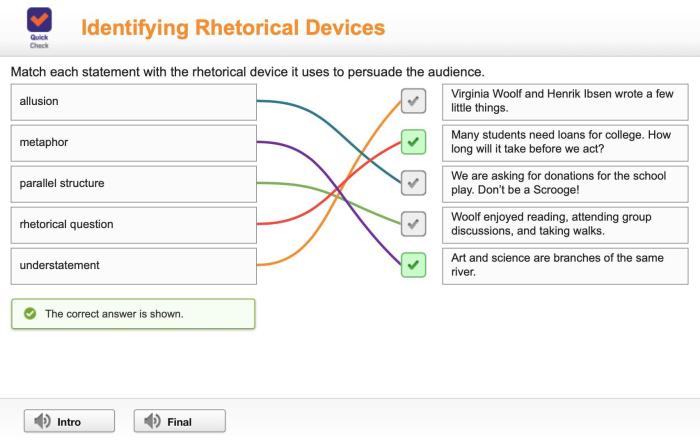
Match each type of factorial design to the correct definition. – Match each type of factorial design to the correct definition, a crucial aspect of research and experimentation, sets the stage for understanding the intricacies of factorial designs. Factorial designs, with their ability to investigate multiple factors simultaneously, hold immense significance in various fields, unraveling the complex interplay of variables.
Delving into the depths of factorial designs, we will explore their types, definitions, and the rationale behind matching each type to its corresponding definition. Furthermore, we will shed light on the applications of factorial designs, showcasing their versatility in research and industry.
1. Types of Factorial Designs
Factorial designs are a powerful statistical tool that allows researchers to investigate the effects of multiple factors simultaneously. They are particularly useful when the factors are expected to interact with each other.
The most common types of factorial designs are 2×2, 3×3, and 2×3 designs. In a 2×2 design, two factors are each tested at two levels. In a 3×3 design, three factors are each tested at three levels. In a 2×3 design, two factors are tested at two levels and one factor is tested at three levels.
Examples of Factorial Designs
- A researcher is interested in investigating the effects of temperature and fertilizer on plant growth. They conduct a 2×3 factorial design, with temperature tested at two levels (low and high) and fertilizer tested at three levels (none, low, and high).
- A marketing manager is interested in investigating the effects of price and advertising on sales. They conduct a 3×2 factorial design, with price tested at three levels (low, medium, and high) and advertising tested at two levels (low and high).
- A manufacturing engineer is interested in investigating the effects of temperature, pressure, and time on the strength of a material. They conduct a 2x2x3 factorial design, with temperature tested at two levels (low and high), pressure tested at two levels (low and high), and time tested at three levels (short, medium, and long).
2. Definitions of Factorial Designs
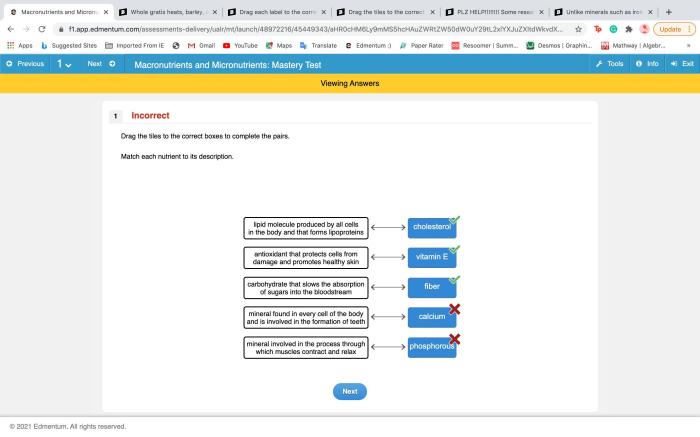
A factorial design is a statistical design in which two or more factors are varied simultaneously. Each factor has two or more levels, and the experiment is conducted at all possible combinations of the levels of the factors.
Key Characteristics of Factorial Designs, Match each type of factorial design to the correct definition.
- Factors:The independent variables in a factorial design.
- Levels:The different values that a factor can take.
- Treatments:The different combinations of levels of the factors.
Importance of Randomization and Replication in Factorial Designs
Randomization and replication are two important principles of factorial design. Randomization ensures that the subjects in the experiment are assigned to treatments randomly, which helps to control for confounding variables. Replication ensures that the results of the experiment are reliable, which helps to rule out the possibility that the results are due to chance.
3. Matching Factorial Designs to Definitions
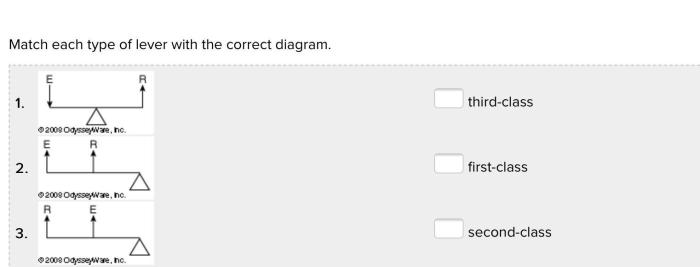
| Type of Factorial Design | Definition |
|---|---|
| 2×2 | A factorial design in which two factors are each tested at two levels. |
| 3×3 | A factorial design in which three factors are each tested at three levels. |
| 2×3 | A factorial design in which two factors are tested at two levels and one factor is tested at three levels. |
4. Applications of Factorial Designs
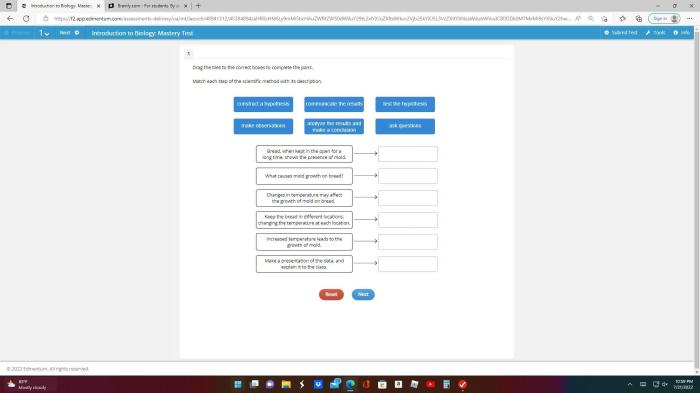
Factorial designs are used in a wide variety of research and industry applications. Some common applications include:
- Investigating the effects of multiple factors simultaneously:Factorial designs allow researchers to investigate the effects of multiple factors simultaneously, which can be more efficient and cost-effective than conducting separate experiments for each factor.
- Identifying interactions between factors:Factorial designs can help researchers identify interactions between factors, which can provide valuable insights into the complex relationships between variables.
User Queries: Match Each Type Of Factorial Design To The Correct Definition.
What is the purpose of matching factorial design types to definitions?
Matching factorial design types to definitions establishes a clear understanding of each design’s characteristics and capabilities, enabling researchers to select the most appropriate design for their research objectives.
How does understanding factorial design definitions enhance research?
Understanding factorial design definitions empowers researchers to interpret experimental results accurately, draw valid conclusions, and make informed decisions based on their findings.