Dna genes and chromosomes worksheet – Delve into the fascinating world of DNA, genes, and chromosomes with this comprehensive worksheet. Discover the intricate structure of DNA, the blueprints of life, and the role of genes in heredity. Explore the mechanisms of DNA replication, gene expression, and genetic variation, gaining a profound understanding of the fundamental processes that govern all living organisms.
1. DNA Structure and Function
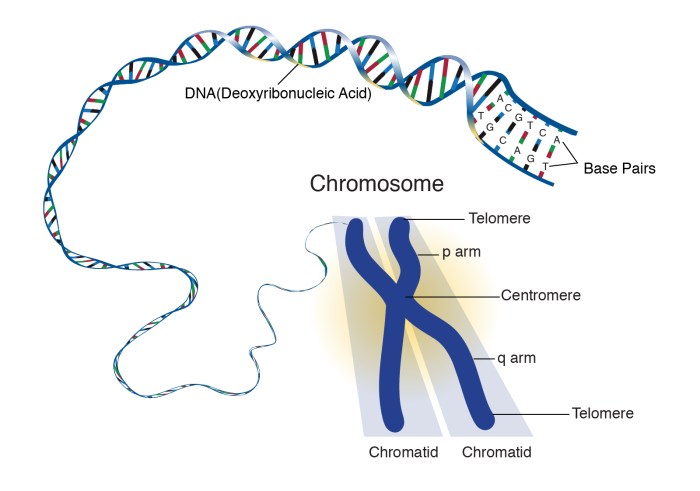
DNA, the molecule of life, holds the genetic instructions for all living organisms. It consists of two long chains of nucleotides, arranged in a double helix shape. Each nucleotide contains a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
These bases pair up according to specific rules: A with T and G with C, forming hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together. DNA stores genetic information in the sequence of these bases, which serves as a blueprint for the development and functioning of an organism.
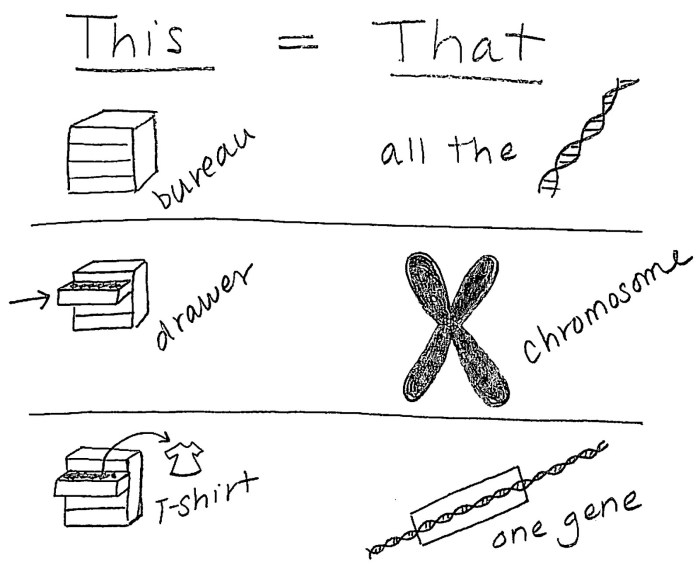
2. Genes and Chromosomes
Genes are specific regions of DNA that code for proteins or RNA molecules. They are located on chromosomes, which are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of cells. Each chromosome contains many genes, arranged in specific locations called loci. Chromosomes play a crucial role in cell division and inheritance, ensuring that genetic information is passed on accurately from one generation to the next.
3. DNA Replication and Gene Expression
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It involves the enzyme DNA polymerase, which reads the existing DNA strand and synthesizes a new complementary strand. Gene expression is the process by which the information encoded in DNA is used to produce proteins or RNA molecules.
It involves two main steps: transcription, where the DNA sequence is copied into RNA, and translation, where the RNA sequence is used to assemble amino acids into proteins.
4. Genetic Variation and Inheritance
Genetic variation is the presence of differences in DNA sequences between individuals. It can arise from mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence, or polymorphisms, which are variations in the DNA sequence that do not alter the function of the gene.
Genetic variation is essential for evolution, as it provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon. Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring. It is governed by the laws of Mendelian genetics, which describe the patterns of inheritance for specific traits.
5. DNA Technology and Applications: Dna Genes And Chromosomes Worksheet

DNA technology encompasses a range of techniques that allow us to manipulate and analyze DNA. These techniques include PCR (polymerase chain reaction), DNA sequencing, and genetic engineering. DNA technology has revolutionized fields such as medicine, forensics, and biotechnology, and has applications in areas such as disease diagnosis, DNA fingerprinting, and gene therapy.
As DNA technology continues to advance, it is likely to have an even greater impact on our lives in the years to come.
General Inquiries
What is the basic structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helix molecule composed of two strands of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine.
How do genes differ from chromosomes?
Genes are specific regions of DNA that code for proteins or RNA molecules, while chromosomes are organized structures that contain multiple genes and other genetic material.
What is the process of DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix and the synthesis of new strands complementary to the existing ones.
