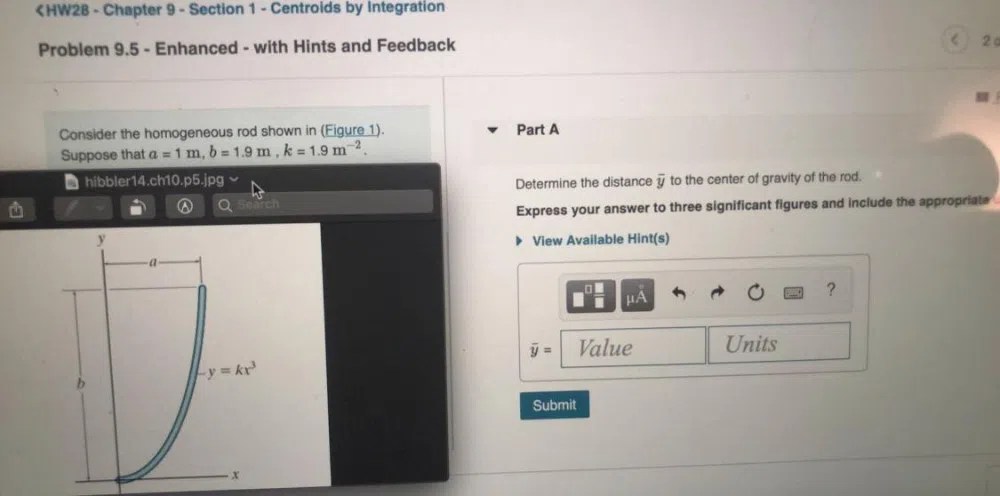
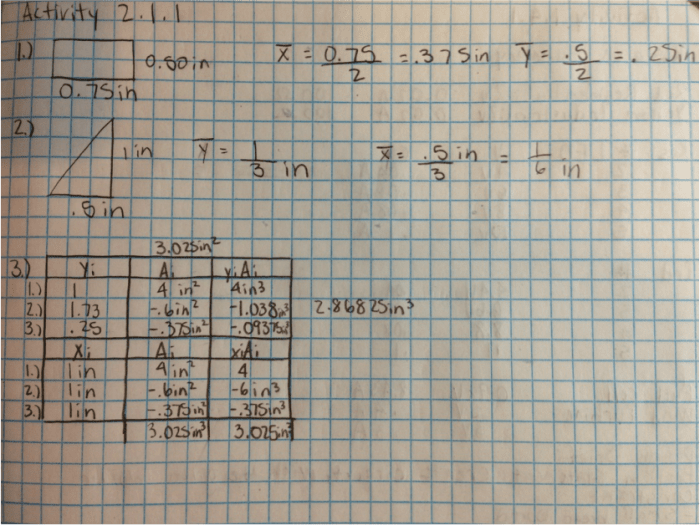Activity 2.1 1 centroids answer key – In this in-depth exploration, we delve into the enigmatic world of centroids, their profound significance in data analysis, and their diverse applications across various fields. From the intricacies of their calculation to their visualization techniques, we uncover the nuances of centroids, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental concept.
Activity 2.1 Centroids: Activity 2.1 1 Centroids Answer Key
Centroids, also known as geometric centers, are pivotal points that represent the average location of a set of data points. They play a crucial role in data analysis, providing insights into the central tendency and distribution of data.
Calculating centroids involves different methods depending on the data type. For instance, the centroid of a set of points in a Euclidean space can be determined by finding the average of their coordinates along each dimension. In contrast, for non-Euclidean data, such as categorical data, alternative methods like medoids are employed.
Applications of Centroids
Centroids find applications in various fields, including:
- Clustering:Centroids serve as cluster centers in clustering algorithms, partitioning data into distinct groups based on similarity.
- Data Visualization:Centroids aid in visualizing data by providing a central point of reference, enabling the identification of patterns and trends.
- Machine Learning:Centroids are utilized in machine learning models, such as k-means clustering, to optimize the grouping of data points.
Limitations and Challenges, Activity 2.1 1 centroids answer key
While centroids offer valuable insights, they also have limitations:
- Sensitive to Outliers:Outliers can significantly influence the location of centroids, potentially misrepresenting the true center of the data.
- Dimensionality:Calculating centroids for high-dimensional data can be computationally intensive and may not accurately capture the data’s distribution.
Alternatives to Centroids
Alternative methods to centroids include:
- Medoids:Medoids are robust alternatives to centroids, less susceptible to outliers and suitable for non-Euclidean data.
- K-means Clustering:K-means clustering assigns data points to clusters based on their proximity to cluster centers, providing a more nuanced representation of data distribution.
- Hierarchical Clustering:Hierarchical clustering creates a hierarchical structure of clusters, offering insights into the relationships between different data points.
Visualizing Centroids
Centroids can be visualized using:
- Scatter Plots:Centroids can be plotted as points on scatter plots, providing a visual representation of their location relative to the data points.
- Cluster Plots:Centroids can be used to create cluster plots, where data points are colored according to their assigned cluster, highlighting the centroid’s role in cluster formation.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of centroids in data analysis?
Centroids serve as representative points that provide insights into the central tendency and distribution of data, enabling researchers to identify patterns, make inferences, and draw meaningful conclusions.
How are centroids calculated for different types of data?
The calculation of centroids varies depending on the data type. For numerical data, the mean is typically used, while for categorical data, the mode or median may be more appropriate.
What are the limitations associated with using centroids?
Centroids may not accurately represent the distribution of data in the presence of outliers or when the data is not normally distributed.